Last updated on June 1st, 2024 at 08:14 am
It should come as no surprise that what you eat affects both your body and mind. New studies are demonstrating a deeper connection between diet and mental health, according to a developing area of study called nutritional psychiatry. Harvard Medical School from Harvard University and many other respectable educational institutions have written about this in the last five years or so. We are going to share some superfoods that can enhance both the body and mind.
Studies are showing links between a healthy gut and the manner in which the immune system functions. Additionally, studies show that poor gut health not purely contributes to poor mental wellness but also raises the chance of developing other illnesses.
What we consume has an effect on our digestive health. The “hormone of happiness” (or “happy hormone”) known as serotonin is then released when the correct foods are consumed. This neurotransmitter must be present in the appropriate amounts to keep your mood upbeat, your sleep patterns regular, and your general health on track. For some, exploring hormone replacement therapy online can further support overall well-being by addressing hormonal imbalances.
Want to know how to maintain a healthy gut and mind? The most recent research is shared below, along with information on foods that can help you stay healthy physically and psychologically.
Here are some examples of how eating well might improve your mental health…
What Relationship Does Nutrition Have with Mental Health?
Approximately 95 percent of the body’s serotonin is produced inside the stomach. It is this molecule that controls hunger, sleep, and mood. The diversity of the gut’s essential bacteria is lost when it is not fed the right, healthy nutrients. Serotonin levels may consequently drop as a result.
Growing amounts of studies are being done in the field of medicine on the relationship between intestinal health and overall health. Based on a recent Harvard Health article, chronic diseases can result from an imbalance of good and bad gut bacteria.
Such illnesses include, for instance:
● Anxiety
● Asthma
● Diabetes
● Obesity
● Metabolic syndrome
● Inflammatory bowel disease
● Depression
However, the effect of food on mood is most notable. Researchers, as we stressed, are investigating nutritional tackles to prevent and resolve mental problems in the relatively new discipline of psychology known as nutritional psychiatry. It turns out that having a healthy gut with beneficial bacteria affects digestion, as well as body inflammatory processes, energy, and mood.
The trillions of microorganisms that reside in your intestines are known as the “gut microbiome”, and this research is helping them learn more about it. The digestive system contains between 300 and 500 distinct types of bacteria, and a healthy gut requires a diversity of good bacteria.
For those seeking additional support for joint and digestive health, consider incorporating BPC-156 into your wellness routine. This peptide, available in different dosages and time-release formulas, is designed to provide targeted support where it’s needed most.
What Indicates That Gut Is Healthy?
As was already noted, an appropriate proportion of bacteria, viruses, and fungi is necessary for the gut microbiome. When you are born, you are first exposed to germs. Research shows that a person’s particular gut microbiota develops throughout the initial 1,000 days of existence.
Due to the diversity of bacteria in the gut, it is critical to have a wide range of helpful bacteria to maintain both intestinal and mental health. This can lead to a number of chronic health issues, such as sadness or anxiety when it goes out of balance and persists for too long. A balance in gut health may be caused by antibiotic use and/or a poor diet that is not nutritious and varied.
Strong defenses against poisons and bacteria considered “bad” are built by good bacteria. Additionally, it reduces inflammation, aids in nutritional absorption, and stimulates neurological connections between the intestines and the brain. How diverse the microbiota in your gut is depends on what foods you eat all over the course of your life. Your digestive system and overall health will benefit from a balanced diet reduced in food that is processed and refined sugars.

What Lies Beneath the Connection Between Gut and Mood?
The hormone known as serotonin affects both motor and emotional functions. Additionally, it is regarded as a natural mood balancer.
Your gut microbiome’s health has an impact on how much serotonin along with other neurotransmitters are generated. A lack of energy and other psychological problems could result from a serotonin deficiency.
Insufficient serotonin may also contribute to psychological problems like:
● Depression
● Anxiety
● Insomnia
● Aggression
● Poor memory
● Irritability
● Impulsive behavior
● Low self-esteem
The health issues listed above underscore the importance of gut health for mental wellness. If you are feeling physically poorly as a result of poor eating, they may also be magnified. Think about the ways your mental health might be affected the following time you reach for the bowl of office sweets (one day after another) or use the services of a fast-food’s drive-through.
Additional evidence for the significance of gut health includes the following:
● Less inflammation is a result of healthy gut flora.
This also lessens inflammation elsewhere in the body. Both your mental and physical well-being are likely to suffer if your gut is not in good shape. Inflammation has been related to depression in research, which may help to explain why conventional antidepressants sometimes do not work.
● Whole foods could boost your mood.
Whole foods are helpful, according to studies. When compared to diets high in processed foods and sugar, healthy eating habits such as practicing the Mediterranean diet can lower the likelihood of depression by 25–35%.
● “Brain fog” might result from a bad diet.
“Brain fog”, which is a feeling of confusion, disorientation, and a loss of “sharpness”, is another relationship between the brain and nutrition. A bad diet or dehydration may also be responsible for this.
● “Antidepressant foods” could be beneficial.
An Antidepressant Food Scale of 12 antidepressant nutrients associated with the prevention and treatment of depression is described in a 2018 study that was published in the World Journal of Psychiatry. Mussels, oysters, watercress, salmon, romaine lettuce, spinach, cauliflower, and strawberries are a few examples of foods that contain these nutrients.
● Eat healthfully to lower inflammation.
According to a 2018 study released in Molecular Psychiatry, adopting a nutritious, balanced diet such as the Mediterranean diet while limiting foods that cause inflammation may help prevent depression.
Things to Consider for a Happy Belly
Consuming a healthier diet is the easiest way to get a healthy stomach; the one that prioritizes whole foods while minimizing processed meals. Lean meats, lower sugar, and fat intake, and choosing high-fiber foods can all be beneficial.
Other dishes and concepts to try include:
● Foods high in probiotics.
Gut health may be supported by plain yogurt without added sugars, fermented beverages, and foods like kefir (unsweetened), sauerkraut, or kimchi.
● Plenty of water.
Drinking plenty of water helps maintain gut health because it keeps the digestive tract functioning. Sports drinks and sweetened waters are excluded.
● Eating should be joyful.
It has been demonstrated that eating slowly and completely supports good digestion and improves absorption.
● General health.
Your gut health can also be impacted by lack of sleep and stress. Sleeping patterns might also suffer from excessive stress. To lessen stress, strive for between 7 and 8 hours each night and include relaxation techniques.
6 Superfoods to Improve Mental Performance
By consistently including essential nutrients such as antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals in your diet, you can enhance crucial brain functioning. So, we scratched the surface now, as well as in earlier parts of the article – it is time to be specific on these superfoods.
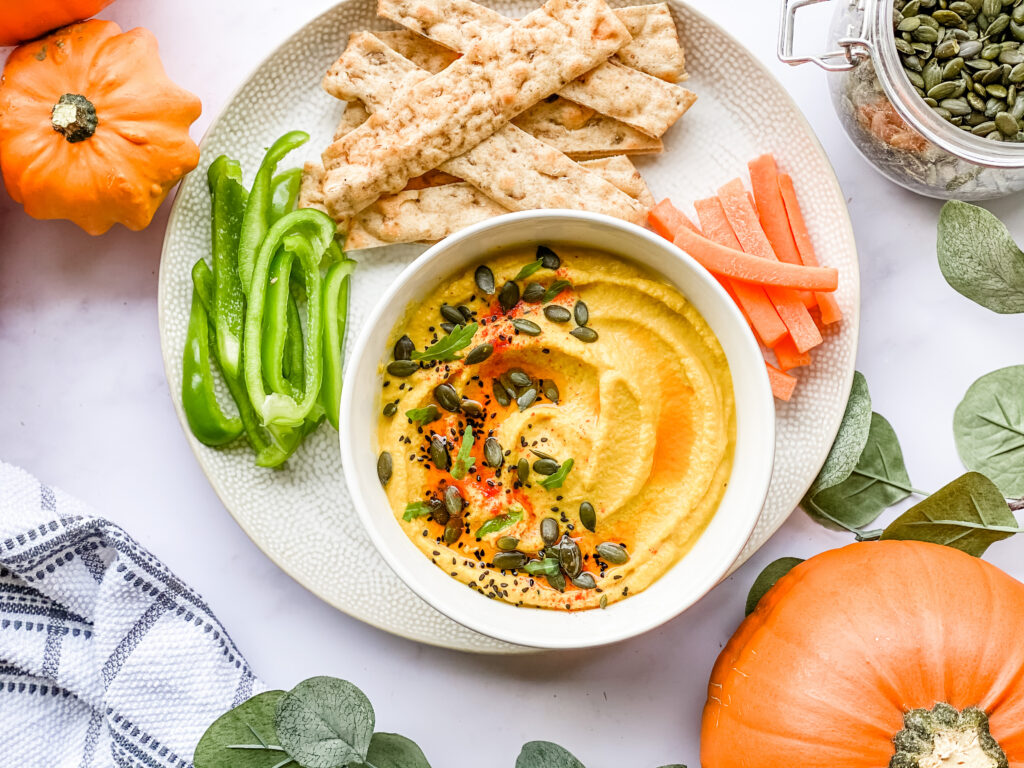

# 1 Pumpkin Seeds: A Repository of Beneficial Nutrients
Brain processes can be hampered by free radicals. Resembling this, micronutrients are crucial for maintaining several neural processes, including mental wellness. Micronutrient- and antioxidant-rich pumpkin seeds pick up free radicals to safeguard the brain.
● Alzheimer’s disease and other disorders are less likely to develop thanks to copper’s enhancement of neurological processes. Copper is found in pumpkin seeds, which benefits mental health.
● Pumpkin seed zinc supports nerve health and may shield against a number of neurological conditions.
● Iron protects against the decline of intellectual functions. Iron is found in pumpkin seeds, which promotes mental health.
● The magnesium in the seeds of pumpkin is essential for the brain and memory. Migraines, epilepsy, and depression can result from a lack of it.
# 2 A Powerful Curcumin Supplier for the Brain: Turmeric
Stress is decreased and inflammation is controlled by turmeric in the body. It has curcumin as an active component, which can pass the blood-brain barrier and enter the brain directly.
● Aids brain cell growth: Turmeric’s curcumin increases the release of growth hormone, which aids in the development of new brain cells. It might have advantages by delaying the aging-related decline in mental abilities.
● Battles depression: Curcumin uplifts mood and lessens the effects of depression by promoting the generation of serotonin and dopamine.
● Enhances memory: According to a promising study, turmeric curcumin may improve memory in those who have Alzheimer’s disease.
# 3 Grass-Leafed Veggies: The Power of Antioxidants and Nutrients
Green leafy veggies have a number of health benefits. Common green vegetables have a wealth of beneficial vitamins and antioxidants that improve mental health while enhancing brain functions. Involve kale, broccoli, spinach, or cabbage in various combinations. You can prepare shakes that have these leafy greens for breakfast. For lunch, you can combine them with fatty fish (about this a bit later) or incorporate them in a range of meal kit types – from 30-minute kits to ready meals – ordered from meal delivery services (such as Home Chef). Of course, you can put these veggies in a salad for dinner along with your favorite dressing.
● Vitamin K, which promotes brain functioning and guards against free radical damage, is found in leafy foods like mustard greens.
● Lutein: Spinach contains a number of antioxidants, including lutein. Cognitive function deterioration is halted by lutein.
● Folic acid: Leafy green vegetables like spinach have high folic acid content, which helps to battle depression. Additionally beneficial for improving focus and minimizing the impact of free radicals is folic acid.
# 4 Berries: Brain-Boosting Neuroprotectants
Superfoods like blueberries, blackberries, and strawberries are excellent for your brain’s wellness. Berries improve brain and memory processes and aid in memory maintenance.
Because of the polyphenol in these fruits, they have a detoxifying effect. The brain’s aging processes may be postponed by this chemical’s cleansing and recycling effects.
# 5 Whole Grains to Stabilize Your Mood
Because complex carbohydrates like whole grains release glucose gradually, they are good for mental health. The consistent flow of energy to the brain contributes to mood stabilization and the absence of unfavorable emotions like rage, irritability, and depression.
Complex carbs and fiber included in whole grains help to keep people calm and cheerful. To increase the intake of complex carbohydrates in your diet, you can think about including whole wheat, brown rice, and oats.
# 6 Great Source of Omega-3 Fats: Fish
Omega-3 fatty acids, which are essential for the growth and operation of the brain, are found in fatty seafood like salmon and sardines. Omega-3 fatty acids support the growth of new brain cells. Additionally, they aid in the enhancement of nerve activities. Fatty fish are superfoods that improve memory and support general brain health.
Omega-3 fatty acids help the brain develop and lessen the symptoms of depression, ADHD (attention deficit hyperactivity disorder), and other mental health issues. Regular consumption of fatty fish might be a great supplement for brain health.
Conclusion
The importance of seeking professional mental health care should not be overlooked, even while a healthier diet may improve moods and general health. It can be precisely what it takes to get your general nutrition and psychological well-being back on track when you combine treatment with lifestyle adjustments.






